Vertebra Analysis
Shuang Liu
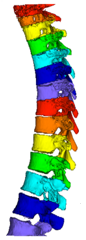 Osteoporosis is a serious and growing public health concern worldwide and is
characterized by low bone mineral density and architectural deterioration of
bone tissue, leading to bone fragility and susceptibility to fracture.
It is estimated that about 75 million people in the United States, Europe and
Japan are affected by osteoporosis.
Osteoporosis is a serious and growing public health concern worldwide and is
characterized by low bone mineral density and architectural deterioration of
bone tissue, leading to bone fragility and susceptibility to fracture.
It is estimated that about 75 million people in the United States, Europe and
Japan are affected by osteoporosis.
Vertebral compression fractures are common in the elderly, accounting for
approximately 1.5 million vertebral compression fractures occur every year in
the US, which have the potential to cause significant disability and morbidity,
as well as incapacitating back pain for many months.
The purpose of this study was to develop a fully automated framework for vertebra
analysis on low-dose chest CT (LDCT), which consists of the following four
stages:
- The individual vertebrae are segmented and labeled with anatomical names
based on image intensity profile analysis and the spatial constraints established
upon other pre-identified organs and structures including clavicles, ribs, sternum
and lungs [2].
- The cortical closed surface of each segmented vertebral body is obtained by
employing progressive surface resolution (PSR) algorithm [1].
- The compression fracture is detected based on image intensity and texture
feature analysis of the segmented cortical surface.
- The osteoporosis is detected based on bone mineral density assessed in the
volume of interest surrounded by the segmented cortical surface.
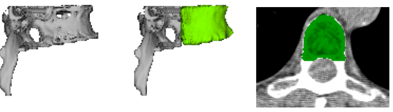 The vertebra segmentation and labeling was validated with 1270 LDCT scans
through visual evaluation and achieved satisfactory performance in 89.9% of the
scans [2]. The PSR algorithm was applied to the cortical surface segmentation of
460 vertebral bodies on 46 LDCT images [1]. For the visual evaluation, the
algorithm achieved acceptable segmentation for 99.35% vertebral bodies.
Quantitative evaluation was performed on 46 vertebral bodies and achieved
overall mean Dice coefficient of 0.939 (with max = 0.957, min = 0.906 and
variance = 0.011) using manual annotations as the ground truth.
The vertebra segmentation and labeling was validated with 1270 LDCT scans
through visual evaluation and achieved satisfactory performance in 89.9% of the
scans [2]. The PSR algorithm was applied to the cortical surface segmentation of
460 vertebral bodies on 46 LDCT images [1]. For the visual evaluation, the
algorithm achieved acceptable segmentation for 99.35% vertebral bodies.
Quantitative evaluation was performed on 46 vertebral bodies and achieved
overall mean Dice coefficient of 0.939 (with max = 0.957, min = 0.906 and
variance = 0.011) using manual annotations as the ground truth.
Presentations and Publications
- Liu, S., Xie, Y. & Reeves, A. P.
Automated 3D closed surface segmentation: application to vertebral body
segmentation in CT image. J Comput Assist Radiol Surg.,11(5), pp.789-801,
2016.
- Liu, S., Xie, Y., & Reeves, A. P.
Individual bone structure segmentation and labeling from low-dose Chest CT.
Proceedings of SPIE Medical Imaging, submitted, March 2017.
List of Current Research Projects
|

 Osteoporosis is a serious and growing public health concern worldwide and is
characterized by low bone mineral density and architectural deterioration of
bone tissue, leading to bone fragility and susceptibility to fracture.
It is estimated that about 75 million people in the United States, Europe and
Japan are affected by osteoporosis.
Osteoporosis is a serious and growing public health concern worldwide and is
characterized by low bone mineral density and architectural deterioration of
bone tissue, leading to bone fragility and susceptibility to fracture.
It is estimated that about 75 million people in the United States, Europe and
Japan are affected by osteoporosis.
 The vertebra segmentation and labeling was validated with 1270 LDCT scans
through visual evaluation and achieved satisfactory performance in 89.9% of the
scans [2]. The PSR algorithm was applied to the cortical surface segmentation of
460 vertebral bodies on 46 LDCT images [1]. For the visual evaluation, the
algorithm achieved acceptable segmentation for 99.35% vertebral bodies.
Quantitative evaluation was performed on 46 vertebral bodies and achieved
overall mean Dice coefficient of 0.939 (with max = 0.957, min = 0.906 and
variance = 0.011) using manual annotations as the ground truth.
The vertebra segmentation and labeling was validated with 1270 LDCT scans
through visual evaluation and achieved satisfactory performance in 89.9% of the
scans [2]. The PSR algorithm was applied to the cortical surface segmentation of
460 vertebral bodies on 46 LDCT images [1]. For the visual evaluation, the
algorithm achieved acceptable segmentation for 99.35% vertebral bodies.
Quantitative evaluation was performed on 46 vertebral bodies and achieved
overall mean Dice coefficient of 0.939 (with max = 0.957, min = 0.906 and
variance = 0.011) using manual annotations as the ground truth.